
A research team from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a new method that enhances the accuracy and reliability of trace gas analysis in open-path infrared spectroscopic remote sensing.
Their recent study was published in Analytical Chemistry.
Active infrared optical remote sensing enables real-time, long-distance monitoring of multiple trace gases along open paths. However, interference from water vapor absorption, combined with fluctuations in temperature and humidity, aerosol scattering, and optical turbulence, often leads to non-stationary variations in background spectra. These effects significantly reduce the accuracy of quantitative analysis, posing a major challenge for applying this technology in high-precision measurements.
To address this issue, the researchers developed an integrated retrieval method that combines Variable Decomposition Level Dual-Tree Complex Wavelet Transform (VDL-DTCWT) with Nonlinear Least Squares (NLLS) fitting. The VDL-DTCWT method adaptively reconstructs background signals across spectral bands, robustly extracting multi-scale and non-stationary features.
Meanwhile, the NLLS forward model incorporates common interfering gases such as water vapor as independent absorption components alongside target pollutants, enabling joint inversion and effectively eliminating cross-talk.
Experimental results demonstrate that this method effectively reduces background interference, thereby improving the accuracy and precision of pollutant concentration retrieval under complex environmental conditions.
These findings provide a new solution for quantitative infrared spectral analysis in open-path scenarios and offer important methodological insights for advancing high-precision optical remote sensing in dynamic environments.

Real-time background spectrum synthesis framework based on VDL-DTCWT (Image by QIN Yusheng)
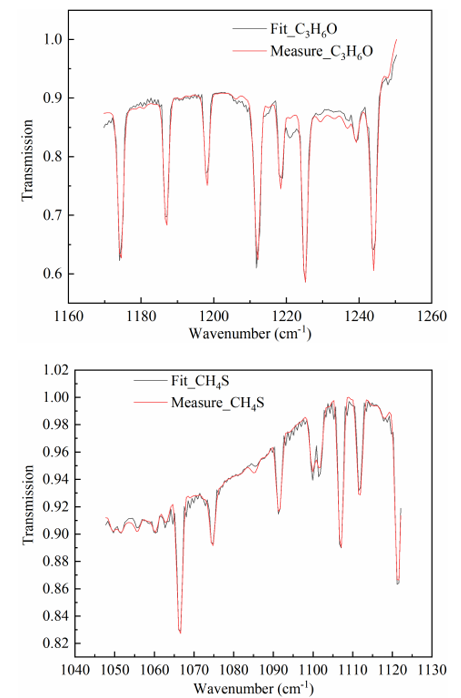
Typical pollutant spectral fitting results (Image by QIN Yusheng)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

